Python
1. 将两个列表合并到一个字典中
假设我们在Python中有两个列表,我们希望将它们合并为字典形式,其中一个列表的项目作为字典的键,另一个作为值。这是在用 Python 编写代码时经常遇到的一个非常常见的问题。
但是为了解决这个问题,我们需要考虑几个限制,比如两个列表的大小,两个列表中项目的类型,以及其中是否有重复的项目,尤其是我们将使用的项目 作为钥匙。我们可以通过使用像 zip 这样的内置函数来克服这个问题。
keys_list = ['A', 'B', 'C']
values_list = ['blue', 'red', 'bold']
# 有 3 种方法可以将这两个列表转换为字典
# 1.使用Python zip、dict函数
dict_method_1 = dict(zip(keys_list, values_list))
# 2. 使用带有字典推导式的 zip 函数
dict_method_2 = {key:value for key, value in zip(keys_list, values_list)}
# 3.循环使用zip函数
items_tuples = zip(keys_list, values_list)
dict_method_3 = {}
for key, value in items_tuples:
if key in dict_method_3:
pass
else:
dict_method_3[key] = value
print(dict_method_1)
print(dict_method_2)
print(dict_method_3)
结果如下:

2.将两个或多个列表合并为一个列表
当我们有两个或更多列表时,我们希望将它们全部收集到一个大列表中,其中较小列表的所有第一项构成较大列表中的第一个列表。
例如,如果我有 4 个列表 [1,2,3]、[‘a’,‘b’,‘c’]、[‘h’,‘e’,‘y’], 和[4,5,6],我们想为这四个列表创建一个新列表;它将是 [[1,‘a’,‘h’,4], [2,‘b’,‘e’,5], [3,‘c’,‘y’,6]] 。
def merge(*args, missing_val = None):
max_length = max([len(lst) for lst in args])
outList = []
for i in range(max_length):
outList.append([args[k][i] if i < len(args[k]) else missing_val for k in range(len(args))])
return outList
merge([1,2,3],['a','b','c'],['h','e','y'],[4,5,6])
结果如下:
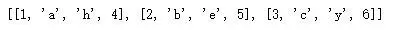
3. 对字典列表进行排序
下一组日常列表任务是排序任务。根据列表中包含的项目的数据类型,我们将采用稍微不同的方式对它们进行排序。让我们首先从对字典列表进行排序开始。
dicts_lists = [
{
Name: James,
Age: 20,
},
{
Name: May,
Age: 14,
},
{
Name: Katy,
Age: 23,
}
]
# 方法一
dicts_lists.sort(key=lambda item: item.get(Age))
# 方法二
from operator import itemgetter
f = itemgetter('Name')
dicts_lists.sort(key=f)
结果如下:
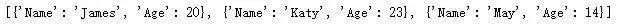
4. 对字符串列表进行排序
我们经常面临包含字符串的列表,我们需要按字母顺序、长度或我们想要或我们的应用程序需要的任何其他因素对这些列表进行排序。现在,我应该提到这些是对字符串列表进行排序的直接方法,但有时您可能需要实现排序算法来解决该问题。
my_list = [blue, red, green]
# 方法一
my_list.sort()
my_list = sorted(my_list, key=len)
# 方法二
import locale
from functools import cmp_to_key
my_list = sorted(my_list, key=cmp_to_key(locale.strcoll))
结果如下:
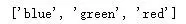
5. 根据另一个列表对列表进行排序
有时,我们可能想要/需要使用一个列表来对另一个列表进行排序。因此,我们将有一个数字列表(索引)和一个我想使用这些索引进行排序的列表。
a = ['blue', 'green', 'orange', 'purple', 'yellow']
b = [3, 2, 5, 4, 1]
sortedList = [val for (_, val) in sorted(zip(b, a), key=lambda x: x[0])]
print(sortedList)
结果如下:
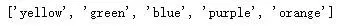
6. 将列表映射到字典
如果给定一个列表并将其映射到字典中。也就是说,我想将我的列表转换为带有数字键的字典,应该怎么做呢?
mylist = ['blue', 'orange', 'green']
#Map the list into a dict using the map, zip and dict functions
mapped_dict = dict(zip(itr, map(fn, itr)))
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「程序猿-小菜」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_61655732/article/details/120636340
